|
Treatment of Non Small CEll Lung
Cancer (NSCLC)
Surgery
Surgery is the best treatment for
limited lung cancer. Resection usually includes the entire lung, a
lung’s lobes (most used), or a lobe segment. Patients with advanced
cancer or metastatic disease rarely gain from surgery. In very
specific and rare cases, resection of limited primary lung tumor and
single distant metastasis may be considered.
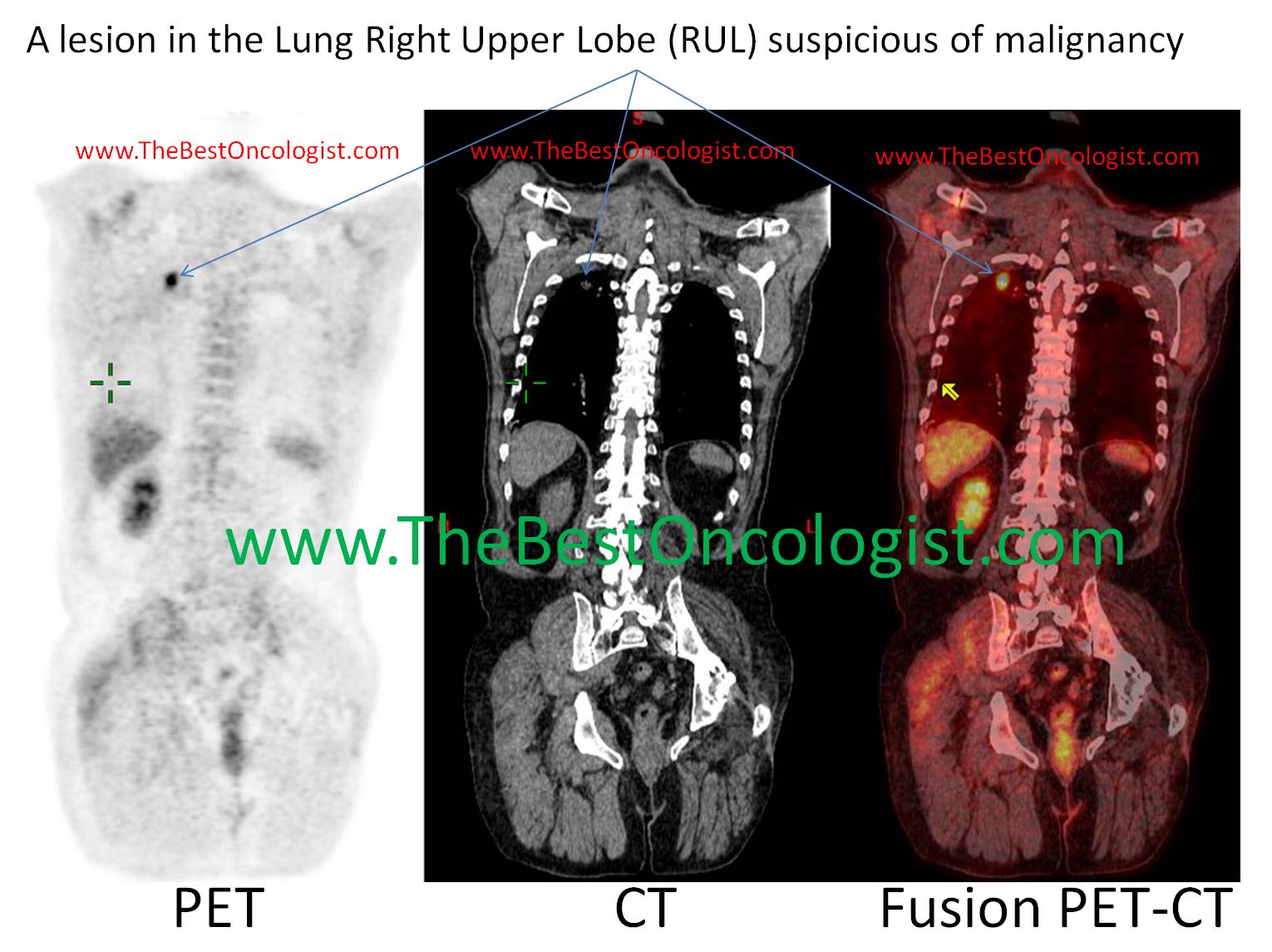
A patient with lung cancer
with a localized lesion in the Right Upper Lobe (RUL) which can be
cured with surgery or Stereotactic Body RadioTherapy- SBRT
Radiotherapy
Radiotherapy is a pivotal modality
for the treatment of lung cancer. It is used both for curative and
palliative treatments. Radiotherapy is also used preoperatively in
some patients (with or without chemotherapy) to shrink the tumor
size so that surgery become feasible. Side effects of radiotherapy
include toxicity to: the normal lung tissue (radiation pneumonitis),
heart, esophagus (esophagitis) and spinal cord. These toxicities are
more prominent with increased radiation dose and/or intensity, and
in patients undergoing concomitant chemotherapy and radiation.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for NSCLC usually
includes combination of drugs containing cisplatin (or carboplatin).
Other drugs used together with platinum include etoposide,
paclitaxel, vinorelbine or gemcitabine. Chemotherapy improve
survival in metastatic disease, as well as in locally advanced
disease. Recently, clinical trails showed that the use of
chemotherapy after resection of lung cancer, improve the survival of
patients. Overall, chemotherapy (platinum based) have a role in
treatment of lung cancer, but the prognosis for the long term,
remains disappointing.
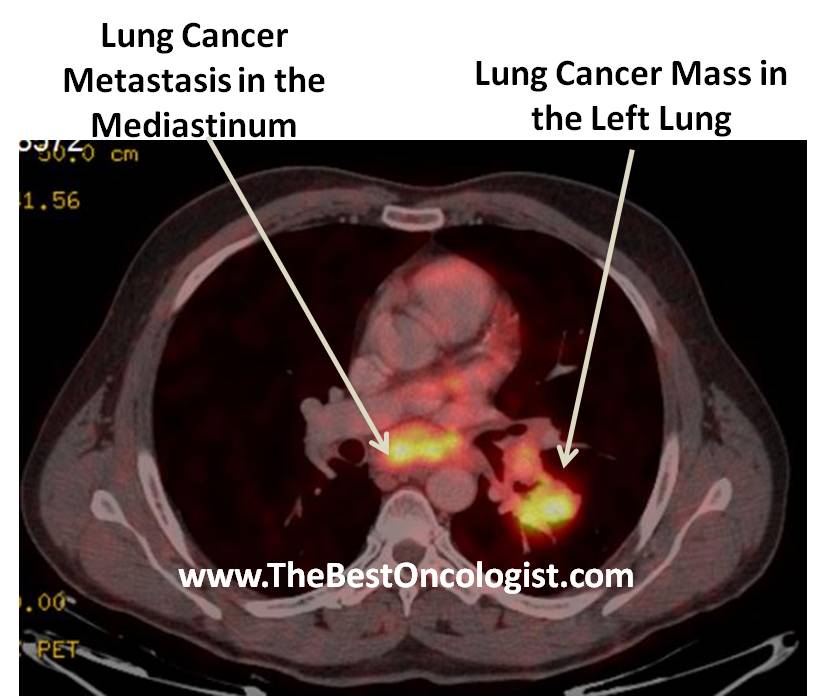
A patient with lung cancer
with a tumor in the left lung and metastatic spread to the
mediastinum which can be ideally treated with chemo-radiotherapy
Biologic therapy
1)
Bevacizumab (Avastin): Avastin is used in
treatment of advanced non squamous NSCLC (stage III, IV). In
squamous cell lung cancer, avastin resulted in high rate of
pulmonary hemorrhage (12) and hence its use was restricted to non
squamous non-small-cell-lung-cancer. Phase III study by Sandler et
al. (5) showed that adding bevacizumab to paclitaxel and carboplatin
compared to paclitaxel and carboplatin alone resulted in
prolongation of median survival from 10.3 months to 12.3 months.
There was though a 6 fold increase in significant bleeding, a 10
fold increase in severe hypertension, and a higher rate of febrile
neutropenia in the group that received
paclitaxel-carboplatin-bevacizumab compared to the
paclitaxel-carboplatin control group (5). Interestingly, women who
participated in this trail didn't benefit from avastin, with median
overall survival of 13.1 months in the paclitaxel-carboplatin group,
compared to 13.2 months in the paclitaxel-carboplatin-bevacizumab
group (5).
Treatment
of
Small Cell Lung Cancer
Surgery
SCLC usually develops in the central
airways. Most patients present with metastatic disease. Surgery
usually is not applicable to most patients, except for patients with
“very limited’ and operable disease.
Radiation
Radiotherapy is integral part of the
treatment of SCLC (limited disease). Prophylactic radiation to the
brain is used in some patients, especially in near or complete
responders to induction chemotherapy.
Radiation also plays a pivotal role
in palliation (e.g. radiotherapy to painful bone lesion).
Chemotherapy
Several drugs have a role in
treatment of SCLC. Cisplatin or carboplatin are usually combined
with etoposide (VP-16), and were proved to give favorable results in
limited stage disease. Other regimens of chemotherapy for SCLC
include the ICE protocol (Ifosfamide, Carboplatin, Etoposide), VIP
(VP16=Etoposide, Ifosfamide, Platinol), and cisplatin& Irinotecan.
|